We are investigating vapor pressure to relate it to intermolecular forces. Vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by vapor in a thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases (solid or liquid) at a given temperature in a closed system. The vapor pressure indicates a liquid's evaporation rate. it is realted to the tendency of particles to escape from the liquid (or solid). A substane that has a high vapor pressure at normal temperatures is referred to as volatile. Anne Marie Helmenstine, 2014)
Intermolecular forces are forces of attraction or repulsion which act between neighboring particles (atoms, molecules or ions).
 |
| Schlenk Tube: We put the substance in here and from the schlenk tube we can properly take out all the hair with the vaccum. |
 |
| Water Bath: We use this to heat up the sucstance to the desired temperature. |
 |
| Vaccum Line: We use this to take the air out of the schlenk tube. |
 |
| Vapor Pressure Sensor: We plug this into a laptop and our schlenk tube to record the vapor pressure of our substance. |
 |
| 2-Propanol or Isopropyl alcohol: chemical compound with the molecular formula C3H8O or C3H7OH. It's a colorless, flamavle hemical compound with a strogn odor. it has a melting point of 355.8 K and a molecular mass of 60.  |
 | ||||||||||
|
Table of chemical compounds showing their boiling points, vapor pressure and intermolecular forces.
Name of compound
|
Molecular formula
|
Diagram of structure
|
Boiling point (oC)
|
Temperatures when vapour pressure measured (oC)
|
Vapour pressure (kPa)
|
Types of intermolecular forces
|
Pentane
|
C5H10
|
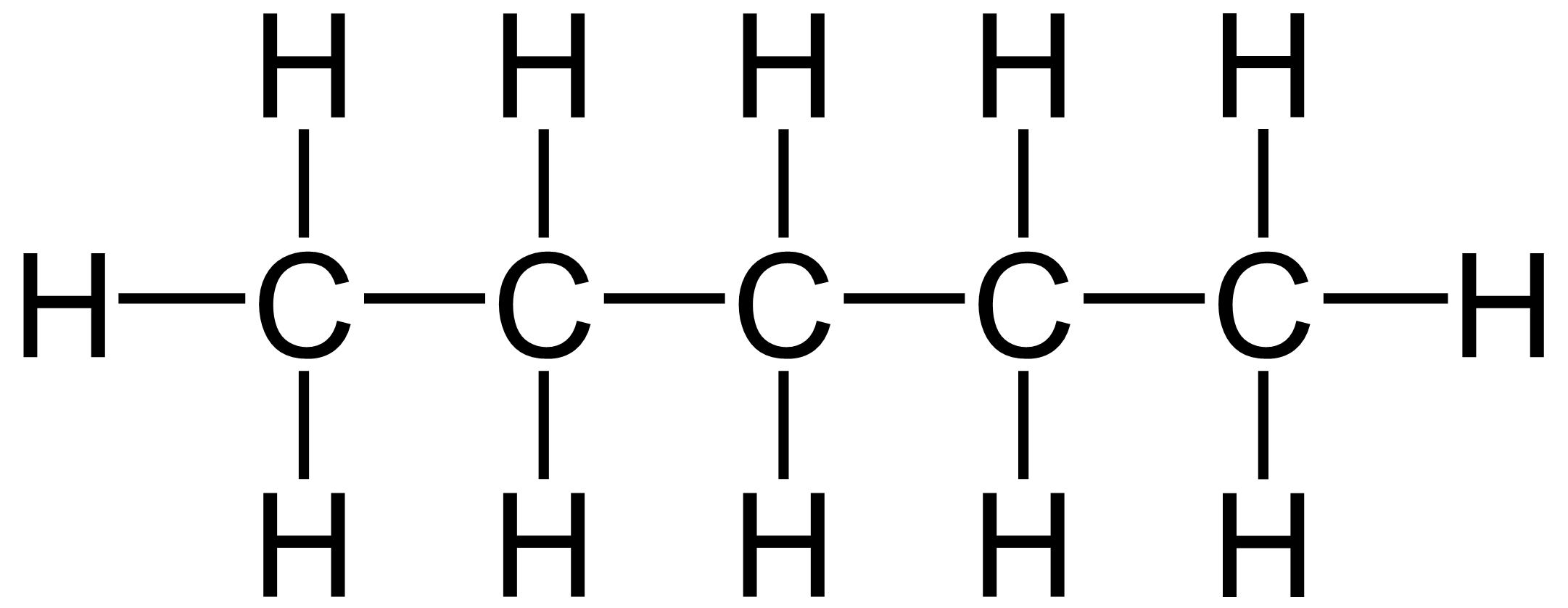 |
36
|
0
15
25
35
|
44.87
47
49.86
54
|
Van der Waal
|
Ethyl acetate
|
C4H8O2
|
 |
77,1
|
0
15
25
35
|
11.75
30.83
30.43
50.47
|
Van der Waal, permanent dipole dipole
|
Butyl acetate
|
C6H12O2
|
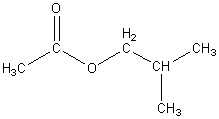 |
127
|
0
15
35
|
0,25
16,18
22,15
26,42
|
Van der Waal, permanent dipole dipole
|
1-Butanol
|
CH3(CH2)3
|
 |
117,7
|
0
15
25
35
|
0.63
1.46
2.72
3.66
|
Van der Waal, permanent dipole dipole, hydrogen
bonding
|
Propyl acetate
|
C5H10O2
|
101.6
|
0
15
25
35
|
9,1
20.66
20.89
21.54
|
Van der Waal, permanent dipole dipole
|
|
2-Propanol
|
C3H8O
|
 |
82
|
0
15
25
35
|
78.99
96.15
100.85
11.29
|
Van der Waal, permanent dipole dipole, hydrogen bonding
|
Explaination:
The boling point of pentane is the lowest one because of the intermolecular force it has. The only intermolecular force that pentane has is Van der Waal, so we can assume that the boiling point of this compound will be at a very low temperature.
The compound witht the highest boling point is butyl acetate, which doesn't have hydrogen bonding, that is the strongest type of bonding. Because of this reason we have to think that the permanent dipole dipole forces of this compound are really high.
1-Butanol and 2-Propanol have all 3 types of forces but their boling point is lower than butyl acetate. so the three forces of this compound must be waker than the two of butyl acetate.
References:
Anne Marie Helmenstine, P. 2014. Vapor Pressure Definition - Chemistry
 Glossary Definition of Vapor Pressure. [online] Available at: http://chemistry
Glossary Definition of Vapor Pressure. [online] Available at: http://chemistry .about.com/od/chemistryglossary/a/vaporpressdef.htm [Accessed: 7 Mar 2014].
.about.com/od/chemistryglossary/a/vaporpressdef.htm [Accessed: 7 Mar 2014].

Intorduction.
ResponderEliminarInclude the graph showing the vapour pressures at 4 different temperatures (of your chemical).
Give the table of class results a title.
Compare the boiling points of the different chemicals and relate them to the intermolecular forecs that each chemical can have.
B - 5 Your information is clearly explained but your must explain your graph of the vapour pressures of your chemical.
ResponderEliminarE - 5 Your graph and table are clear but you must state at which temperatures you carried out the LoggerPro graph in.